When it comes to understanding your server or computer’s inner workings, knowing your CPU’s capabilities is crucial. Enter the lscpu command—a simple yet powerful tool in the UNIX arsenal. Whether you’re a system administrator, a developer, or just a curious tech enthusiast, lscpu offers a window into your machine’s brain.
The Power of lscpu
The lscpu command is your go-to for a quick yet detailed overview of your CPU. It consolidates information from various sources in your system and presents it in a readable format. Think of it as your CPU’s resume, listing everything from its architecture to the number of cores and threads.
Why CPU Information Matters
Why CPU Information Matters
Understanding your CPU’s specs can help you make informed decisions about software installations, performance optimizations, and system upgrades. For instance:
- Performance Tuning: Knowing the number of cores and threads can help you optimize multi-threaded applications.
- Compatibility Checks: Ensuring your software is compatible with your CPU’s architecture and features.
- Upgrade Planning: Deciding whether to upgrade your hardware based on current utilization and future needs.
How to Use lscpu
Using lscpu is as straightforward as it gets. Open your terminal and type:
lscpuHere’s a sample output from the lscpu command:
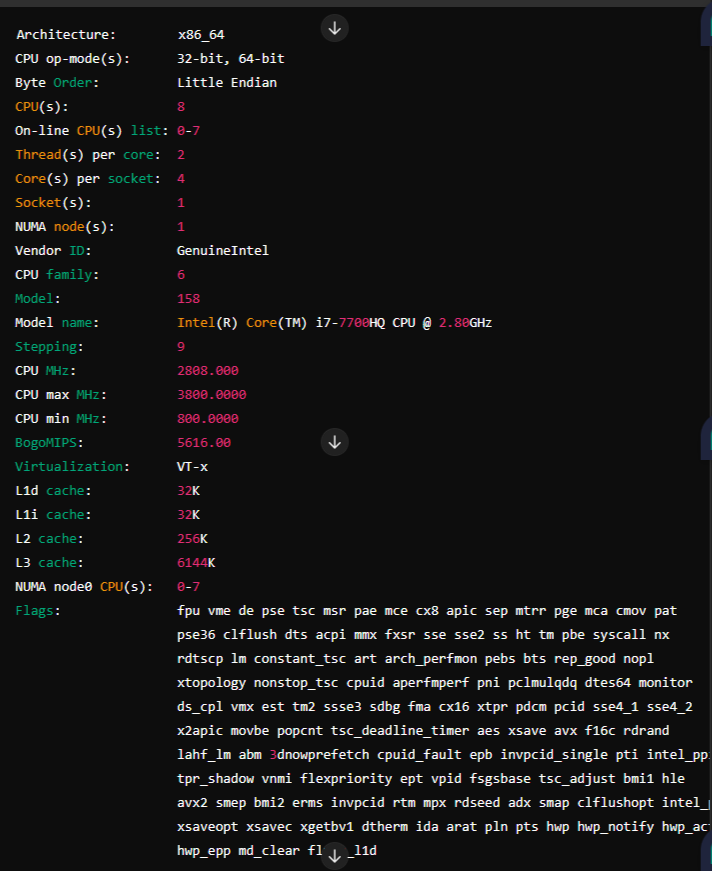
Breaking Down the Output
Let’s decode some of the key sections of this output:
- Architecture: This tells you the type of CPU architecture. Here,
x86_64it indicates a 64-bit architecture. - CPU op-mode(s): Indicates whether your CPU can operate in 32-bit, 64-bit, or both modes.
- CPU(s): Shows the total number of CPUs (or logical cores) available.
- Thread(s) per core: The number of threads that can run on each core. More threads can mean better multitasking.
- Core(s) per socket: The number of cores within a single CPU socket.
- Socket(s): Indicates the number of physical CPU sockets on the motherboard.
- Vendor ID and Model name: Provides the manufacturer and model of the CPU.
- CPU MHz: The current speed of the CPU in MHz. Maximum and minimum speeds are also shown.
- Cache: Information about the different levels of cache memory.
Practical Applications
Imagine you’re planning to deploy a new virtual machine (VM). Knowing the number of cores and the availability of virtualization technology (like VT-x) helps you decide on the right configuration and ensures efficient VM performance. Similarly, if you’re compiling a large codebase, knowing the CPU’s capabilities can help you optimize the build process.
Conclusion
The lscpu command is a powerful yet simple tool that reveals crucial information about your CPU. By understanding and utilizing this data, you can make better decisions about your system’s performance, compatibility, and future upgrades. So next time you’re tweaking your system or planning an upgrade, let lscpu be your guide through the CPU’s inner sanctum. Happy computing!

